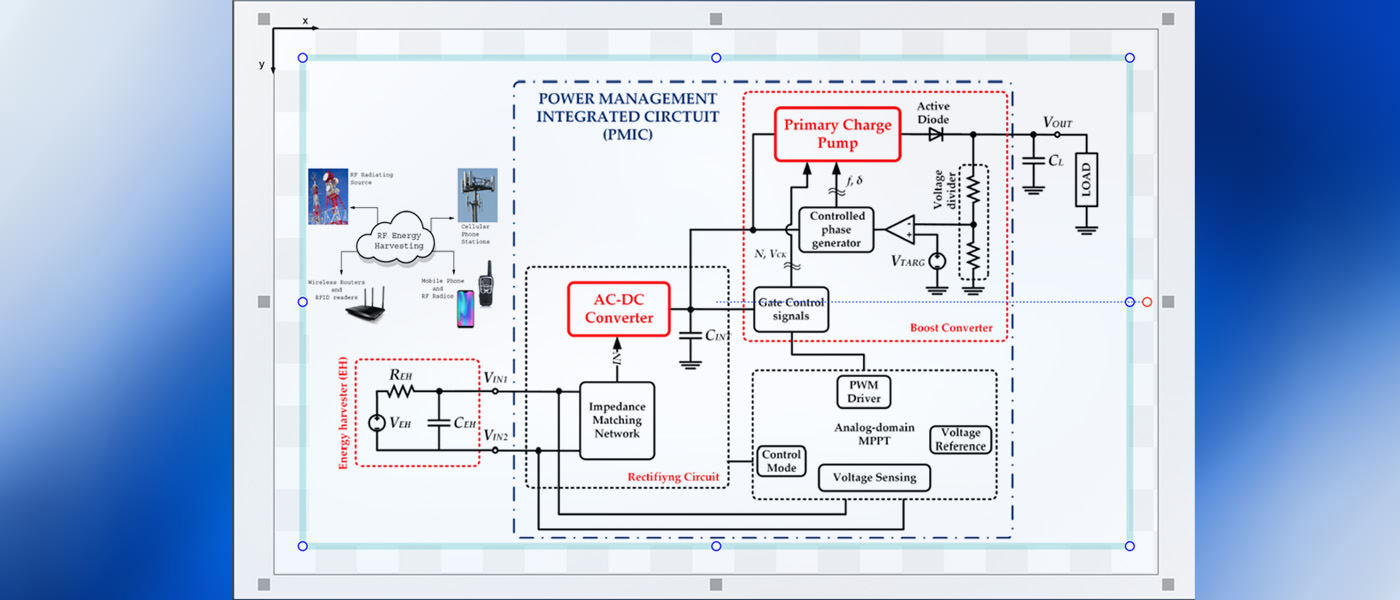
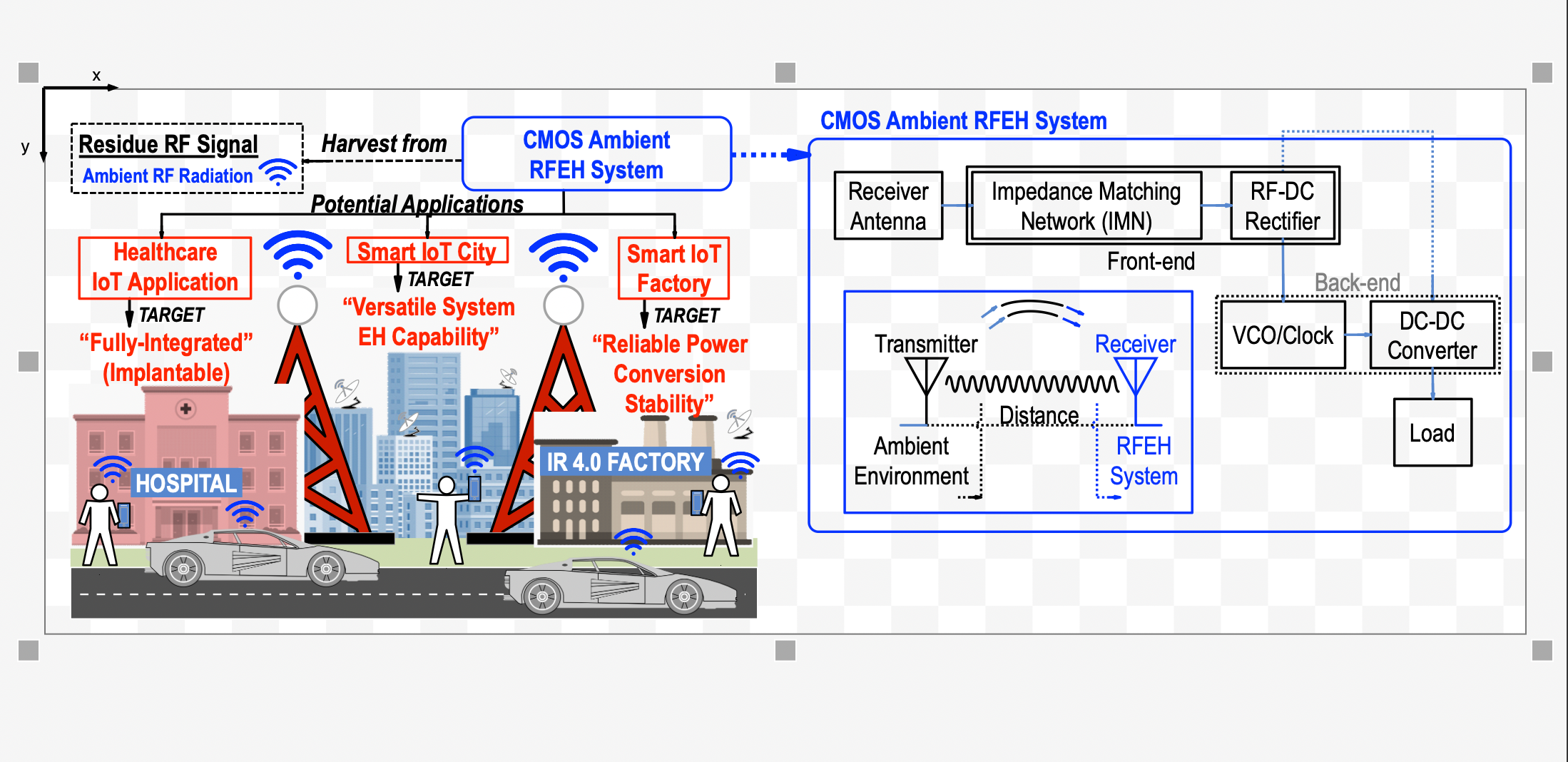
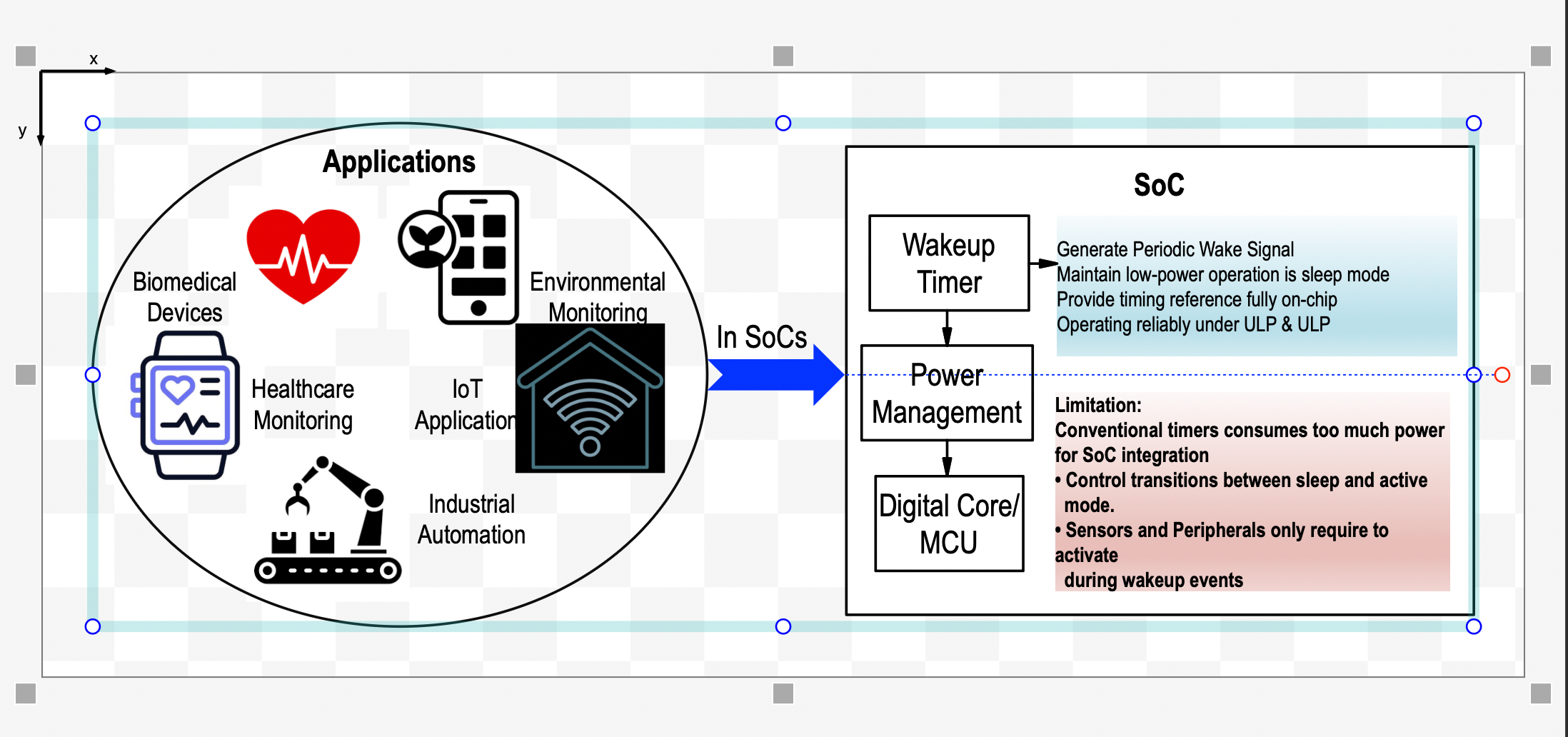
RF energy harvesting (RF-EH) enables compact, self-powered electronics by converting ambient radio signals—emitted by Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks—into usable electrical energy. Unlike solar or motion-based sources, RF can be harvested indoors, in mobile setups, and without line-of-sight, making it ideal for dense, always-connected environments like smart cities, IoT networks, and wearable tech.
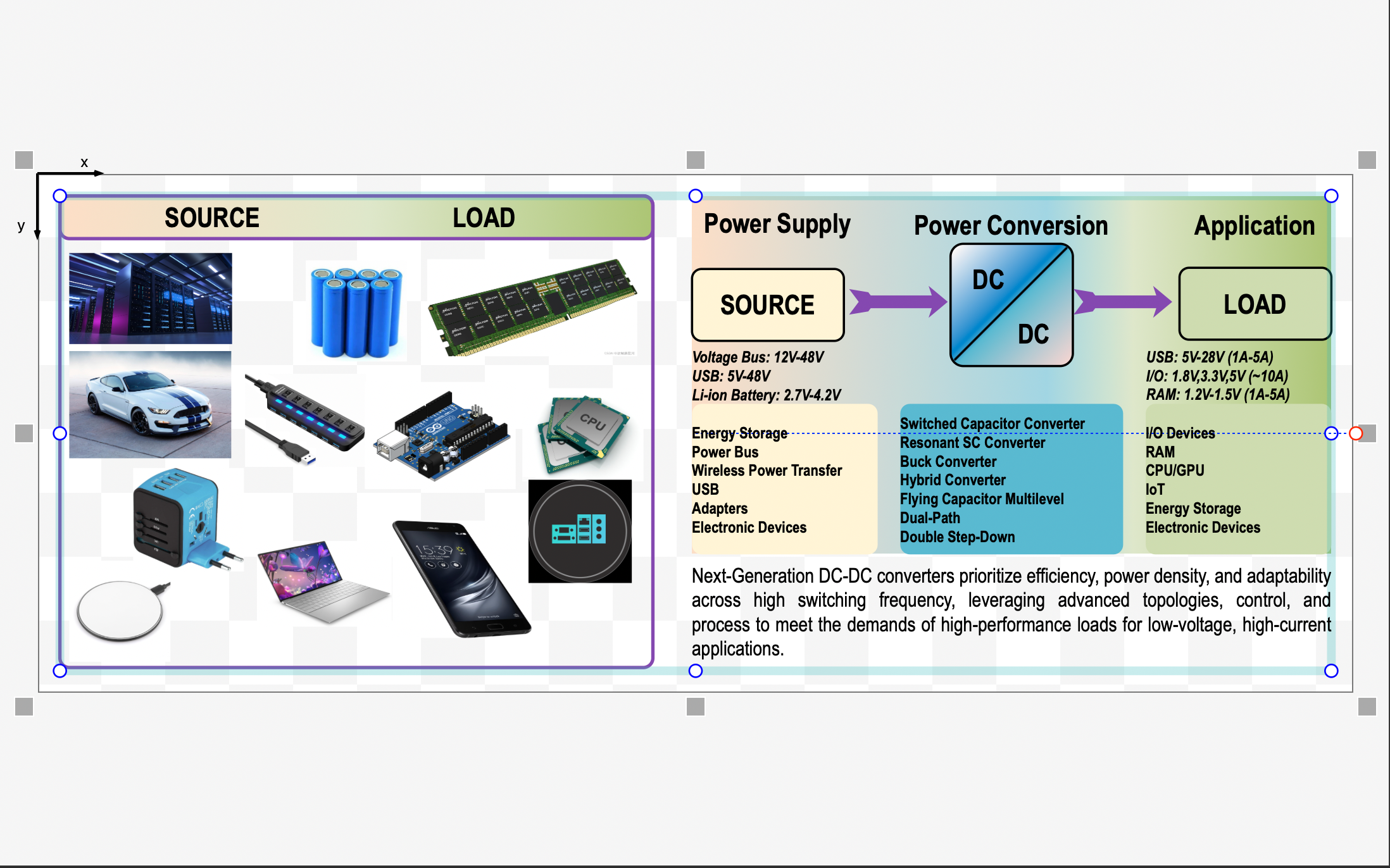
However, harvested RF power is extremely low (typically in the microwatt range), producing sub-volt DC levels (e.g., 100–400 mV), which are too weak to directly power digital circuits. To address this, a Power Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC) is used to boost and regulate the voltage. Charge-pump-based DC–DC converters are particularly well-suited for this task—they work from low voltages, require no inductors, and are fully CMOS-compatible.
The PMIC’s job is twofold: 1) boost low voltage from the RF harvester, and 2) stabilize output for consistent system performance. Advanced PMICs integrate features like adaptive control, maximum power point tracking (MPPT), and dynamic voltage scaling to improve efficiency under fluctuating RF conditions.
When integrated into a System-on-Chip (SoC), the PMIC enables ultra-compact and efficient designs—critical for applications like biomedical implants, asset trackers, and autonomous sensor nodes. Together, RF-EH and SoC-integrated PMICs unlock truly batteryless, maintenance-free operation for next-gen electronic systems.
📌 Main Points :
RF Energy Harvesting (RF-EH) :
- Converts ambient RF signals into usable electrical energy.
- Works indoors and without line-of-sight.
- Ideal for smart cities, IoT devices, and wearables.
Challenge :
RF energy is extremely low (microwatt range, 100–400 mV), too weak for direct digital use.
Role of PMIC (Power Management Integrated Circuit)
- Boosts and regulates the low voltage from RF harvesters.
- Charge-pump DC–DC converters are preferred due to their compatibility and efficiency.
Advanced features include :
- Adaptive control
- Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
- Dynamic voltage scaling
System-on-Chip (SoC) Integration
- Combines RF-EH and PMIC into one chip.
- Enables compact, efficient, and batteryless designs.
Applications
- Biomedical implants
- Asset tracking
- Autonomous sensors
- Maintenance-free IoT devices